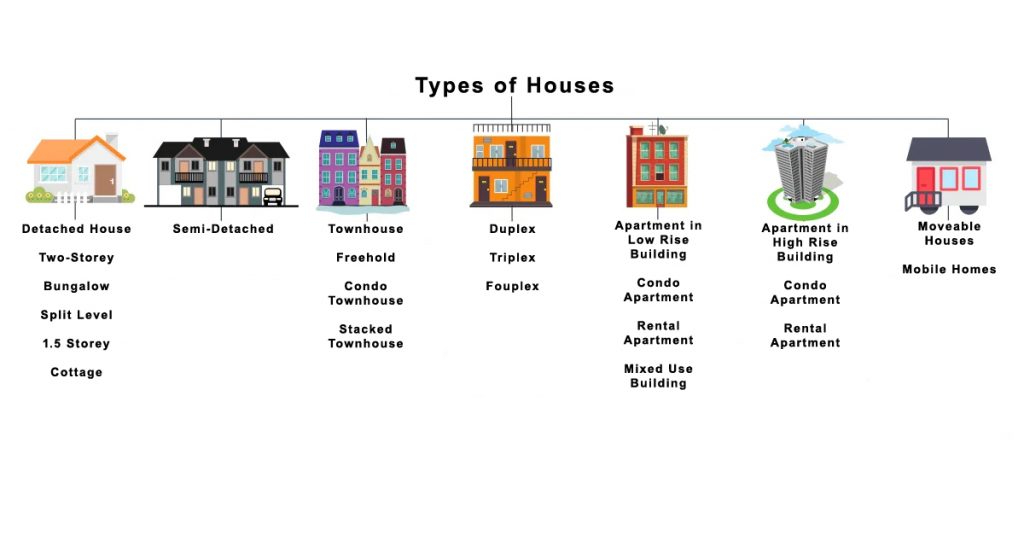
Residential Structures: Single-Family Dwelling Styles
In regards to single-family dwellings, only one dwelling unit is contained in the structure. Below are examples of single family dwellings.
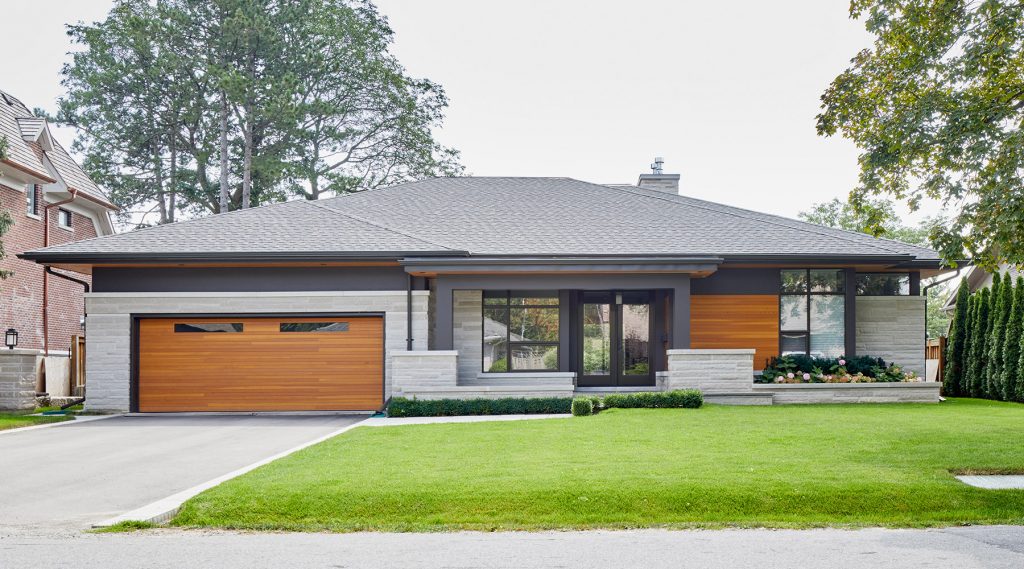

Bungalow – The primary living area is on one floor with few or no stairs. This style is beneficial for those with limited mobility. A bungalow needs a larger lot size in order to provide the same house size as a two-storey home. Variations of bungalows include:
• Ranch Style: This variation of the bungalow offers a larger overall size and typically features an attached garage and a basement. Many of these homes contain approximately 2,000 square feet of living area or more on one floor and are normally oriented horizontally on a lot.
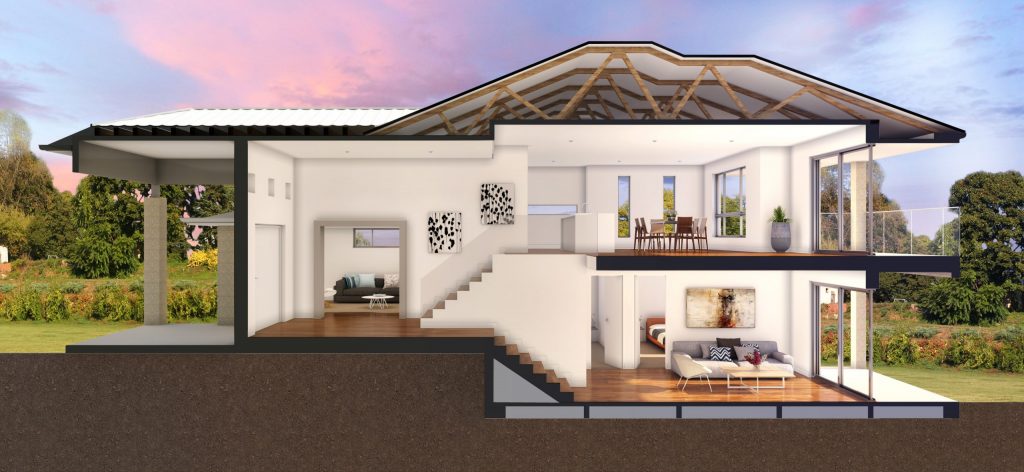

• Bi-Level/Split Entrance: This variation of the bungalow usually has a front entrance at the split between the upper and lower levels. The basement rests at a higher level above grade than other bungalow types which allows for more windows and greater sunlight in the basement area. This has led to the basement area being finished in a similar condition to the main floor, rather than remaining unfinished.

One-and-One-Half Storey – This style of dwelling has about 60% of the overall floor area on the main floor, and features a high-pitched roof, which provides additional living space on the second floor. The roof pitch results in slanted ceilings on the upper level and reduced head clearance. Some styles will include dormers (vertically projecting windows) and may be referred to as a, “Cape Cod” design.
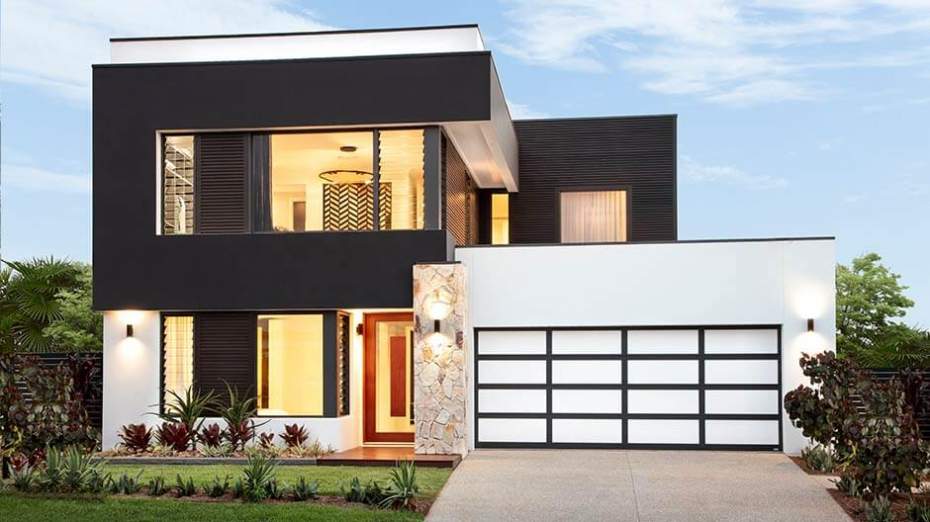

Two-Storey – This style of dwelling is characterized by a combination of an expansive living area and a separate bedroom area level. Bedrooms are on a different level from the rest of the living space. Suitable for families.
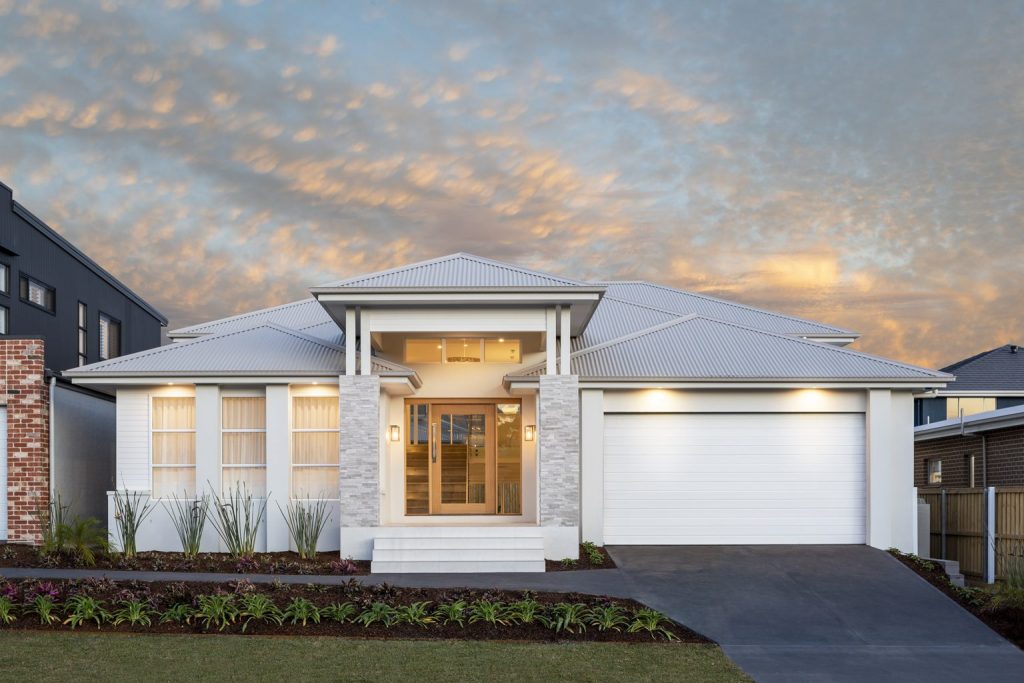

Split Level – This type of dwelling can combine features of other styles, ranging between the bungalow, split-entrance bungalow, and the two-storey home. The ease with which occupants can move from one area of their home to another is a primary characteristic. Side and back splits may have anywhere from three to five levels and are characterized by several sets of stairs. This type of house is a perfect solution for sloping blocks as they are designed to follow the natural slope of the land, resulting in a stunning, architectural split level home that is both unique and spacious.

A Semi-Detached House – (often abbreviated to semi) is a single family duplex dwelling house that shares one common wall with the next house. The name distinguishes this style of house from detached houses, with no shared walls, and terraced houses, with a shared wall on both sides. Semi detached are two distinct homes with separate owners and lots connected through one common wall. They are built side-by-side to each other. Compare that to a duplex which is a property on a single lot with two distinct living spaces and one owner.
Residential Structures: Multi-Unit Dwelling Styles
Buyers wanting to purchase a property where they can live plus generate income by leasing a unit to a tenant, can invest a multi-unit dwelling which are typically converted from a single family or other use to a multi-unit use.
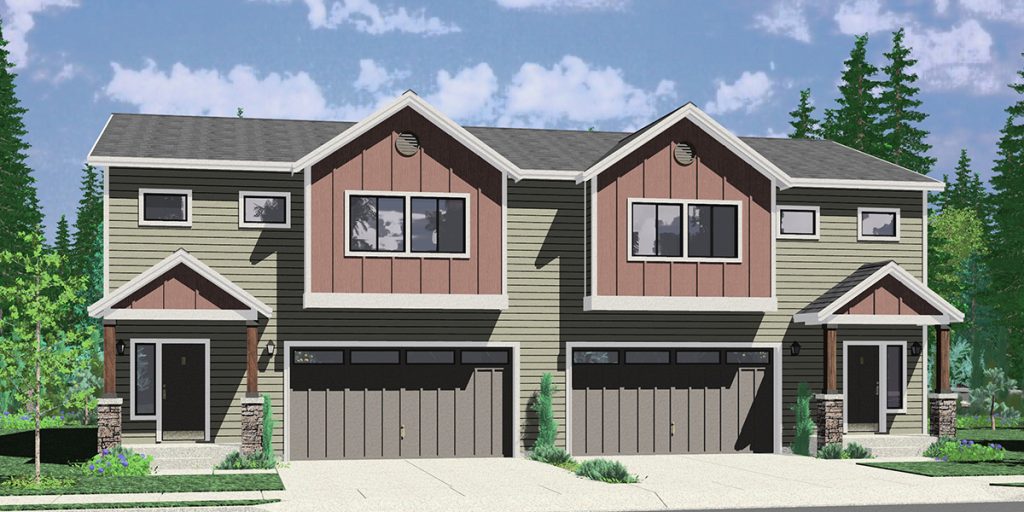

Duplex – A building divided into two individual dwelling units, divided horizontally, as in the style of a two-storey, or vertically as in a bungalow. Each unit can be accessed via a private entrance or a shared entryway. Duplexes (single ownership) are not the same as semi-detached structures (two titles).
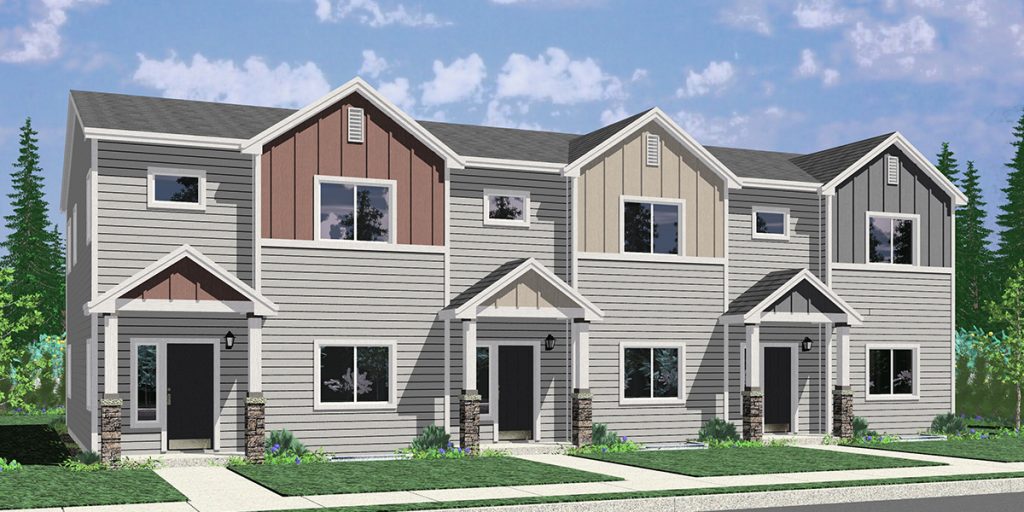

Triplex – A building divided into three individual dwelling units, divided horizontally and/or vertically. Each dwelling can be accessed via a private entrance, a shared entryway, or both.

Fourplex – A building divided into four individual dwelling units and are typically in the style of a bungalow, one-and-one-half storey, or a two-storey dwelling that is divided vertically.
Example chart of various houses in Canada:
Comments are closed

